
This suggests they know how to locate all of the letters on the keyboard, and can press each letter very quickly to type words. Skilled typists can type normal words very fast. If they succeed in doing this, it means the finding can be replicated, and that it happens in more than one lab.įinding from previous resaearch: Prior research showed that typists do something funny. Behmer & Crump repeated an experiment that should also produce this same finding. First we describe an interesting finding from previous research. For example, every time a person types a letter, the timing of the button press and the letter pressed can be measured and stored for later analysis.īehmer & Crump were interested in asking a few different questions, however, we will simplify everything and talk about replication. Typing also happens to be a convenient task for measuring sequencing.
#REPEATED MEASURES ANOVA SPSS SERIES#
Whenever you type a series of letters on the keyboard, you are putting a sequence of actions together, so typing is task that could be used to measure skilled sequencing.
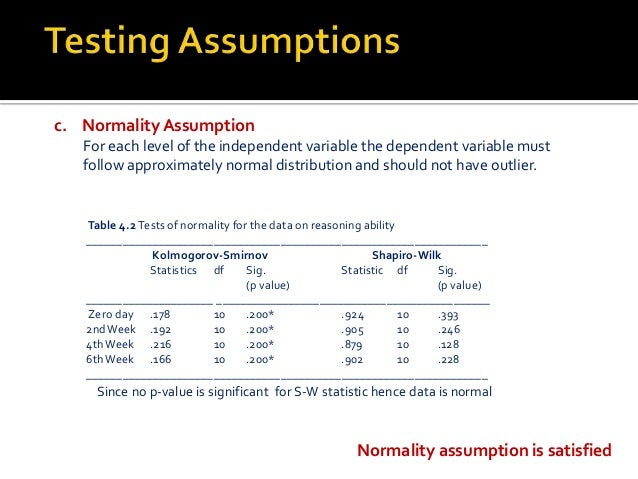
10.6.2 Conduct a Between-Subjects Two-Factor Analysis of Variance (ANOVA).10.4.4 Get the data into the format you want.10.1 Does standing up make you focus more?.9.6.4 Conduct planned comparisons using a paired-samples t-test.9.6.3 Conduct and graph One-Factor Repeated Measures ANOVA.9.6.2 Produce a frequency histogram and remove outliers.9.4.6 Conduct the repeated Measures ANOVA.9.1 Betcha can’t type JHDBZKCO very fast on your first try.8.6.4 Unplanned Comparisons: Post-hoc tests.8.6.2 Performing a One-Factor Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) & Graphing the data.8.1 How to not think about bad memories by playing Tetris.7.6.2 Performing an independent-samples t-test.7.4.7 Reconstructing the graph from the paper.7.4.5 Conduct Independent samples t-test.7.1 Do you come across as smarter when people read what you say or hear what you say?.6.6.5 The relationship between the one-sample and the paired-samples t-test.6.6.3 Performing a paired-samples t-test.6.4.4 Baseline phase: Conduct a one sample t-test.6.1 Does Music Convey Social Information to Infants?.6 Lab 6: t-Test (one-sample, paired sample).5.3.4 Entering data for sign test problems.5.3.2 Calculate difference scores between pairs of measures.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
